Beginning with the roller coaster design worksheet e2020 answers, this guide delves into the captivating world of roller coaster design, providing a comprehensive exploration of its fundamental principles, track design, ride experience, engineering considerations, and historical evolution. Embark on a journey that unravels the secrets behind these thrilling rides, uncovering the intricate details that orchestrate an unforgettable experience.
From understanding the physics of track layout and forces to appreciating the psychological and physiological effects on riders, this guide equips you with a thorough understanding of roller coaster design. Discover the engineering marvels that ensure safety and optimize ride experiences, while tracing the historical trajectory that has shaped this beloved amusement park staple.
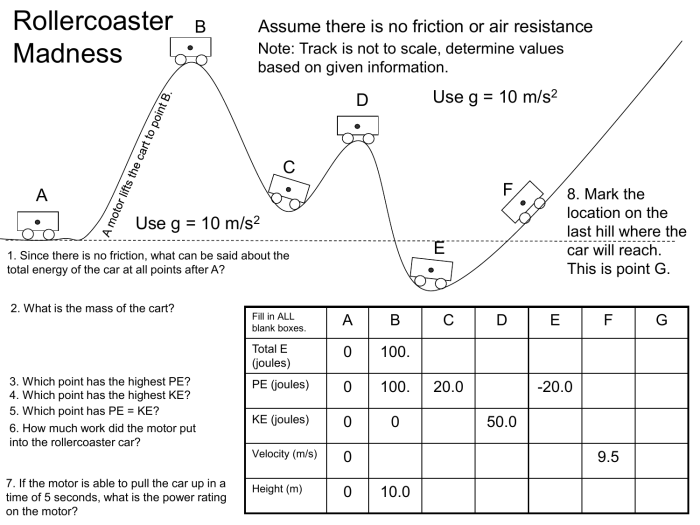
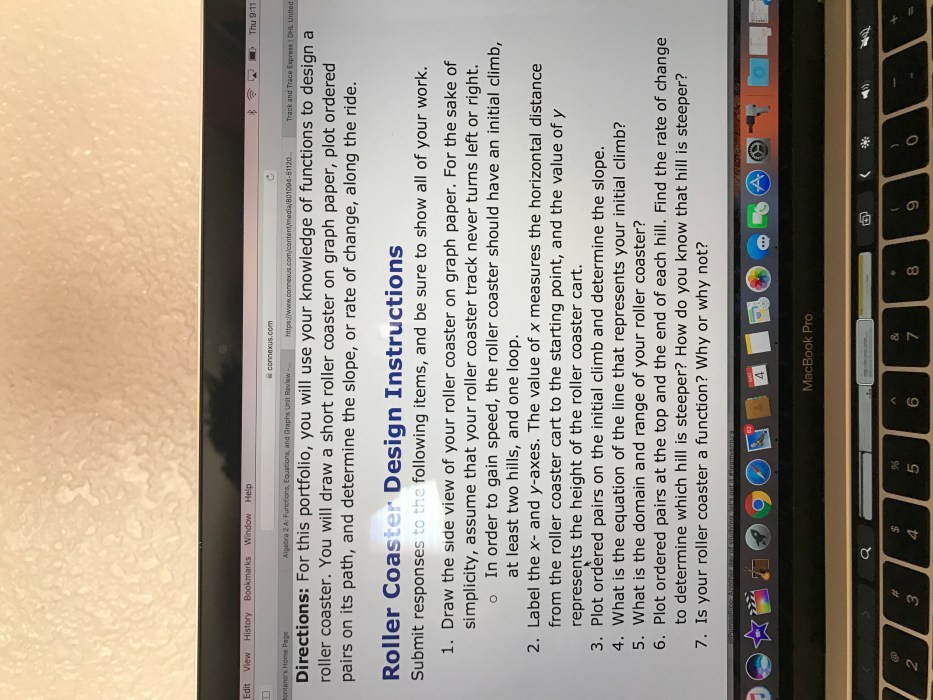
Roller Coaster Design Basics: Roller Coaster Design Worksheet E2020 Answers

Roller coasters are designed to provide a thrilling and exciting experience for riders. The fundamental principles of roller coaster design include track layout, speed, and forces. The layout of the track determines the overall shape and path of the roller coaster, and the speed and forces experienced by riders are determined by the height, length, and curvature of the track.
Types of Roller Coasters
There are three main types of roller coasters: wooden, steel, and hybrid. Wooden roller coasters are the oldest type of roller coaster, and they are typically made from treated wood. Steel roller coasters are made from steel, and they are typically faster and more intense than wooden roller coasters.
Hybrid roller coasters are a combination of wooden and steel, and they offer a unique blend of speed and intensity.
Track Design, Roller coaster design worksheet e2020 answers
The track of a roller coaster is made up of several different components, including curves, hills, and drops. Curves are used to change the direction of the roller coaster, and hills and drops are used to create changes in speed and elevation.
The design of the track is critical to the overall experience of the roller coaster.
There are a number of factors that influence track design, including safety, ride experience, and cost. Safety is the most important factor, and all roller coasters must meet strict safety standards. The ride experience is also important, and designers strive to create roller coasters that are both thrilling and enjoyable.
Cost is also a factor, and designers must balance the cost of construction with the desired ride experience.
| Track Design | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Curves | Change the direction of the roller coaster |
| Hills | Create changes in speed and elevation |
| Drops | Create changes in speed and elevation |
Ride Experience
The ride experience on a roller coaster is determined by a number of factors, including speed, acceleration, and G-forces. Speed is the most obvious factor, and it affects the overall intensity of the ride. Acceleration is the rate at which the roller coaster changes speed, and it can create a feeling of weightlessness or nausea.
G-forces are the forces that are exerted on riders by the roller coaster, and they can cause a variety of physical effects, such as dizziness and blackouts.
The psychological and physiological effects of roller coasters on riders can be significant. Roller coasters can cause a variety of emotions, such as excitement, fear, and exhilaration. They can also cause a number of physical effects, such as increased heart rate, sweating, and nausea.
- Riders should follow all safety instructions
- Riders should not ride if they have any health conditions that could be aggravated by the ride
- Riders should secure all loose items before riding
- Riders should remain seated and keep their hands and feet inside the ride at all times
Engineering Considerations
The structural engineering principles involved in roller coaster design are complex. Roller coasters are subjected to a variety of forces, including gravity, wind, and the weight of the riders. Engineers must design roller coasters that are strong enough to withstand these forces and that are safe for riders.
Computer simulations are used to optimize roller coaster designs. These simulations can help engineers to identify potential problems and to make sure that the roller coaster is safe and enjoyable.
“Engineering considerations are paramount in roller coaster design. We must ensure that our designs are safe and that they provide a thrilling and enjoyable experience for riders.”
– Roller coaster engineer
Historical Evolution
Roller coasters have a long and storied history. The first roller coaster was built in Pennsylvania in 1872, and it was a simple wooden structure. Over the years, roller coasters have evolved significantly, and they now come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Some of the key innovations in roller coaster design include the use of steel, the introduction of inversions, and the development of computer simulations. Steel roller coasters are stronger and faster than wooden roller coasters, and they can be used to create more complex and intense rides.
Inversions are turns that are upside down, and they add an extra level of excitement to roller coasters. Computer simulations have helped engineers to design roller coasters that are safer and more enjoyable.
| Year | Roller Coaster | Impact on Industry |
|---|---|---|
| 1872 | Gravity Pleasure Switchback Railway | First roller coaster |
| 1927 | The Cyclone | First steel roller coaster |
| 1979 | The Revolution | First roller coaster with a vertical loop |
| 2002 | Millennium Force | Tallest and fastest roller coaster in the world at the time |
Query Resolution
What are the key principles of roller coaster design?
Roller coaster design involves understanding track layout, speed, and forces, ensuring a balance between safety, ride experience, and cost.
How do different track components influence the ride experience?
Curves, hills, and drops create varying forces and sensations, contributing to the overall thrill and excitement of the ride.
What are the safety considerations in roller coaster design?
Structural engineering principles, load analysis, and safety factors are crucial in ensuring the integrity and safety of roller coasters.
How has roller coaster design evolved over time?
From early wooden coasters to modern steel and hybrid designs, roller coasters have undergone significant innovations, enhancing speed, height, and ride experiences.